Federal Whistleblower Protections
Date: 2024-10-23
Category: Law Helper
Online HTML Editor powered by CKEditor Online HTML editor user guideReal-time collaboration editor user guide Online HTML Editor Real-time collaboration editor Switch to WYSIWYG editor
In todays complex work environment, the role of whistleblowers is more critical than ever. Federal whistleblower protections are designed to encourage individuals to report wrongdoing without fear of retaliation. This article delves into the intricacies of these protections, the laws that support them, and the impact they have on maintaining integrity within organizations.
Understanding Whistleblowing
What is Whistleblowing?
Whistleblowing refers to the act of reporting misconduct, illegal activities, or unethical behavior within an organization. Whistleblowers play a crucial role in exposing fraud, corruption, and other malpractices, thereby safeguarding public interest and ensuring compliance with the law.
The Importance of Whistleblowers
Whistleblowers are often the first line of defense against corporate and governmental malfeasance. By shedding light on hidden wrongdoings, they help uphold transparency, accountability, and integrity. Their actions can lead to significant reforms, improved safety standards, and the recovery of funds.
Key Federal Whistleblower Protection Laws
Whistleblower Protection Act of 1989
The Whistleblower Protection Act (WPA) is a foundational law that protects federal employees who disclose evidence of illegality, waste, fraud, abuse, or threats to public health and safety. The WPA prohibits retaliation against whistleblowers, ensuring that they can report wrongdoing without fear of losing their jobs or facing other adverse actions.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
Enacted in response to corporate scandals like Enron and WorldCom, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act offers protections for employees of publicly traded companies. SOX mandates that companies create mechanisms for reporting fraud, and it shields employees from retaliation when they report violations of securities laws.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
The Dodd-Frank Act extends protections to whistleblowers in the financial industry. It incentivizes individuals to report securities violations to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) by offering monetary rewards and safeguarding them from retaliation.
The False Claims Act
The False Claims Act allows individuals to sue on behalf of the government if they possess knowledge of fraud against federal programs. Whistleblowers, known as "relators" in this context, can receive a portion of any recovered damages, providing a financial incentive to report fraud.
Scope of Protections
Who is Protected?
Federal whistleblower protections primarily cover federal employees, employees of companies contracting with the government, and employees of publicly traded companies. However, the scope can vary depending on the specific law in question.
Types of Protected Disclosures
Protected disclosures generally include reports of violations of law, gross mismanagement, gross waste of funds, abuse of authority, and substantial and specific dangers to public health or safety. Each law may have specific requirements regarding what constitutes a protected disclosure.
Protection from Retaliation
Retaliation against whistleblowers can take many forms, including termination, demotion, harassment, and blacklisting. Federal laws provide mechanisms for whistleblowers to seek redress, which may include reinstatement, back pay, and compensatory damages.
The Whistleblower Reporting Process
How to Report
Whistleblowers can report wrongdoing through various channels, including internal hotlines, regulatory agencies, and legal counsel. It is crucial for whistleblowers to understand the correct procedures to ensure their disclosures are protected under relevant laws.
The Role of the Office of Special Counsel
The U.S. Office of Special Counsel (OSC) plays a pivotal role in handling whistleblower complaints from federal employees. The OSC investigates claims of retaliation and assists in protecting whistleblowers rights.
Reporting to the Securities and Exchange Commission
Under the Dodd-Frank Act, whistleblowers in the financial sector can report directly to the SEC. The SEC provides an Office of the Whistleblower to manage and respond to these disclosures, ensuring protections and potentially offering financial rewards.
Challenges Faced by Whistleblowers
Legal Obstacles
Navigating the legal landscape can be daunting for whistleblowers. Understanding the nuances of various laws and the specific protections they offer is essential to avoid potential pitfalls.
Fear of Retaliation
Despite legal protections, fear of retaliation remains a significant deterrent for potential whistleblowers. Companies may employ subtle or overt tactics to intimidate individuals considering reporting misconduct.
Emotional and Professional Consequences
Whistleblowers often face emotional stress and professional ramifications. The decision to report wrongdoing can lead to isolation, job loss, or damage to professional relationships.
The Impact of Whistleblower Protections

Enhancing Organizational Integrity
By encouraging transparency and accountability, whistleblower protections strengthen organizational integrity. Companies are more likely to develop robust compliance programs and ethical standards when they know wrongdoing is likely to be reported.
Financial Implications
Whistleblower actions can lead to substantial financial recoveries for governments and stakeholders. For example, under the False Claims Act, billions of dollars have been recovered from fraudulent entities due to whistleblower reports.
Driving Legal and Policy Changes
Whistleblower disclosures have historically led to significant legal and policy changes. They can prompt investigations, lead to reforms, and inspire new legislation aimed at preventing future misconduct.
The Future of Whistleblower Protections
Technological Advancements
As technology evolves, so do the methods for reporting and addressing misconduct. Secure digital platforms for anonymous reporting and AI-driven data analysis could further enhance the effectiveness of whistleblower protections.
Global Perspectives
While this article focuses on U.S. federal laws, whistleblower protections are a global concern. International standards and collaborations may emerge to provide more comprehensive safeguards worldwide.
Ongoing Legislative Efforts
Continuous legislative efforts aim to strengthen existing protections and address emerging challenges. Policymakers must remain vigilant in updating laws to reflect the changing landscape of work and ethics.
Conclusion
Federal whistleblower protections are vital in maintaining ethical standards and accountability within organizations. Despite the challenges whistleblowers face, their courage in reporting wrongdoing contributes to a more transparent and just society. As laws and technologies evolve, it is essential to ensure that these protections remain robust and effective, empowering individuals to speak out against misconduct without fear of retaliation.
1Understanding Federal Wire Fraud: A Comprehensive Guide
2Wire fraud is a serious federal crime in the United States, involving the use of electronic communications to commit fraud. Understanding its intricacies is essential for individuals and businesses alike to prevent becoming either victims or perpetrators. This guide delves into the key aspects of federal wire fraud, its implications, and preventive measures.
3What is Federal Wire Fraud?
45
Federal lawyer wire fraud occurs when someone intentionally uses electronic communications, such as the internet or phone lines, to execute a scheme to defraud someone else of money or property. It falls under 18 U.S.C. § 1343 of the United States Code, which stipulates severe penalties for those convicted.
6Key Elements of Wire Fraud
7To secure a conviction for wire fraud, the prosecution must prove several elements:
8-
9
- Scheme to Defraud: There must be evidence of a deliberate plan to defraud someone. 10
- Intent: The perpetrator must have knowingly intended to deceive for financial gain. 11
- Use of Interstate Wires: The scheme must involve the use of interstate or international wire communications. 12
- Fraudulent Representation: There must be false, fraudulent pretenses or representations involved. 13
Examples of Wire Fraud
15Wire fraud covers a broad range of fraudulent activities, including:
16-
17
- Phishing scams where emails are sent to trick recipients into providing personal information. 18
- Telemarketing schemes that defraud individuals by convincing them to send money or information. 19
- Business email compromise (BEC) where attackers impersonate company executives to request wire transfers. 20
- Internet auction fraud where goods are misrepresented or not delivered. 21
Legal Implications of Wire Fraud
23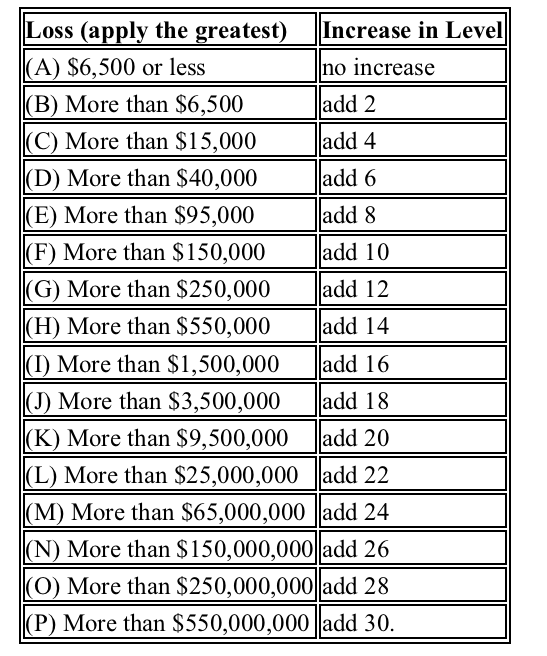
Wire fraud is prosecuted at the federal level and carries significant penalties. Understanding the legal framework can help in recognizing the severity of the crime.
25Penalties for Wire Fraud
26Penalties for a wire fraud conviction can be severe and often include:
27-
28
- Imprisonment: Sentences can extend up to 20 years per count. In cases involving financial institutions, the penalty can rise to 30 years. 29
- Fines: Convicted individuals may face fines reaching up to $250,000, and organizations up to $500,000. 30
- Restitution: Offenders may be ordered to repay victims for their losses. 31